Collections
A collection — sometimes called a container — is simply an object that groups multiple elements into a single unit. Collections are used to store, retrieve, manipulate, and communicate aggregate data. Typically, they represent data items that form a natural group, such as a poker hand (a collection of cards), a mail folder (a collection of letters), or a telephone directory (a mapping of names to phone numbers).
The core collection interfaces encapsulate different types of collections, which are shown in the figure below. These interfaces allow collections to be manipulated independently of the details of their representation. Core collection interfaces are the foundation of the Java Collections Framework. As you can see in the following figure, the core collection interfaces form a hierarchy.
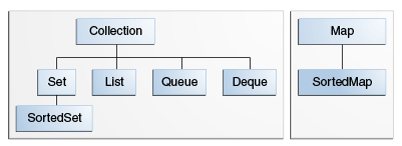
A Set is a special kind of Collection, a SortedSet is a special kind of Set, and so forth. Note also that the hierarchy consists of two distinct trees — a Map is not a true Collection.
The following list describes the core collection interfaces:
A collection — sometimes called a container — is simply an object that groups multiple elements into a single unit. Collections are used to store, retrieve, manipulate, and communicate aggregate data. Typically, they represent data items that form a natural group, such as a poker hand (a collection of cards), a mail folder (a collection of letters), or a telephone directory (a mapping of names to phone numbers).
The core collection interfaces encapsulate different types of collections, which are shown in the figure below. These interfaces allow collections to be manipulated independently of the details of their representation. Core collection interfaces are the foundation of the Java Collections Framework. As you can see in the following figure, the core collection interfaces form a hierarchy.

A Set is a special kind of Collection, a SortedSet is a special kind of Set, and so forth. Note also that the hierarchy consists of two distinct trees — a Map is not a true Collection.
The following list describes the core collection interfaces:
Collection — the root of the collection hierarchy. A collection represents a group of objects known as its elements. The Collection interface is the least common denominator that all collections implement and is used to pass collections around and to manipulate them when maximum generality is desired. Some types of collections allow duplicate elements, and others do not. Some are ordered and others are unordered. The Java platform doesn't provide any direct implementations of this interface but provides implementations of more specific subinterfaces, such as Set and List. Also see The Collection Interface section.
Set — a collection that cannot contain duplicate elements. This interface models the mathematical set abstraction and is used to represent sets, such as the cards comprising a poker hand, the courses making up a student's schedule, or the processes running on a machine. See also The Set Interface section.
List — an ordered collection (sometimes called a sequence). Lists can contain duplicate elements. The user of a List generally has precise control over where in the list each element is inserted and can access elements by their integer index (position). If you've used Vector, you're familiar with the general flavor of List. Also see The List Interface section.
Queue — a collection used to hold multiple elements prior to processing. Besides basic Collection operations, a Queue provides additional insertion, extraction, and inspection operations.
Queues typically, but do not necessarily, order elements in a FIFO (first-in, first-out) manner. Among the exceptions are priority queues, which order elements according to a supplied comparator or the elements' natural ordering. Whatever the ordering used, the head of the queue is the element that would be removed by a call to remove or poll. In a FIFO queue, all new elements are inserted at the tail of the queue. Other kinds of queues may use different placement rules. Every Queue implementation must specify its ordering properties. Also see The Queue Interface section.
Queues typically, but do not necessarily, order elements in a FIFO (first-in, first-out) manner. Among the exceptions are priority queues, which order elements according to a supplied comparator or the elements' natural ordering. Whatever the ordering used, the head of the queue is the element that would be removed by a call to remove or poll. In a FIFO queue, all new elements are inserted at the tail of the queue. Other kinds of queues may use different placement rules. Every Queue implementation must specify its ordering properties. Also see The Queue Interface section.
Deque — a collection used to hold multiple elements prior to processing. Besides basic Collection operations, a Deque provides additional insertion, extraction, and inspection operations.
Deques can be used both as FIFO (first-in, first-out) and LIFO (last-in, first-out). In a deque all new elements can be inserted, retrieved and removed at both ends. Also see The Deque Interface section.
Map — an object that maps keys to values. A Map cannot contain duplicate keys; each key can map to at most one value. If you've used Hashtable, you're already familiar with the basics of Map. Also see The Map Interface section.
The last two core collection interfaces are merely sorted versions of Set and Map:
Deques can be used both as FIFO (first-in, first-out) and LIFO (last-in, first-out). In a deque all new elements can be inserted, retrieved and removed at both ends. Also see The Deque Interface section.
Map — an object that maps keys to values. A Map cannot contain duplicate keys; each key can map to at most one value. If you've used Hashtable, you're already familiar with the basics of Map. Also see The Map Interface section.
The last two core collection interfaces are merely sorted versions of Set and Map:
SortedSet — a Set that maintains its elements in ascending order. Several additional operations are provided to take advantage of the ordering. Sorted sets are used for naturally ordered sets, such as word lists and membership rolls. Also see The SortedSet Interface section.
SortedMap — a Map that maintains its mappings in ascending key order. This is the Map analog of SortedSet. Sorted maps are used for naturally ordered collections of key/value pairs, such as dictionaries and telephone directories. Also see The SortedMap Interface section.
Methods of Collection interface
There are many methods declared in the Collection interface. They are as follows:| No. | Method | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | public boolean add(Object element) | is used to insert an element in this collection. |
| 2 | public boolean addAll(collection c) | is used to insert the specified collection elements in the invoking collection. |
| 3 | public boolean remove(Object element) | is used to delete an element from this collection. |
| 4 | public boolean removeAll(Collection c) | is used to delete all the elements of specified collection from the invoking collection. |
| 5 | public boolean retainAll(Collection c) | is used to delete all the elements of invoking collection except the specified collection. |
| 6 | public int size() | return the total number of elements in the collection. |
| 7 | public void clear() | removes the total no of element from the collection. |
| 8 | public boolean contains(object element) | is used to search an element. |
| 9 | public boolean containsAll(Collection c) | is used to search the specified collection in this collection. |
| 10 | public Iterator iterator() | returns an iterator. |
| 11 | public Object[] toArray() | converts collection into array. |
| 12 | public boolean isEmpty() | checks if collection is empty. |
| 13 | public boolean equals(Object element) | matches two collection. |
| 14 | public int hashCode() | returns the hashcode number for collection. |
Iterator interface
| Iterator interface provides the facility of iterating the elements in forward direction only. |
Methods of Iterator interface
There are only three methods in the Iterator interface. They are:- public boolean hasNext(): it returns true if iterator has more elements.
- public object next() : it returns the element and moves the cursor pointer to the next element.
- public void remove(): it removes the last elements returned by the iterator. It is rarely used.
No comments:
Post a Comment